Vitamin E Complex Reduces Inflammation & Oxidative Stress
Supplementing vitamin E complex including tocopherols and tocotrienols reduces inflammation and oxidative stress. That's the conclusion of two studies, one a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of vitamin E supplementation published in 2020, the other a systematic review of randomized controlled trials of tocotrienol supplementation published in 2021.
These studies support my recommendation to take the Nature's Sunshine Vitamin E Complex and indicate that if you intend to reduce inflammation you may benefit from a significantly higher dosage than I previously recommended. These new studies suggest that higher doses – greater than 700 mg daily – provide the greatest benefits.
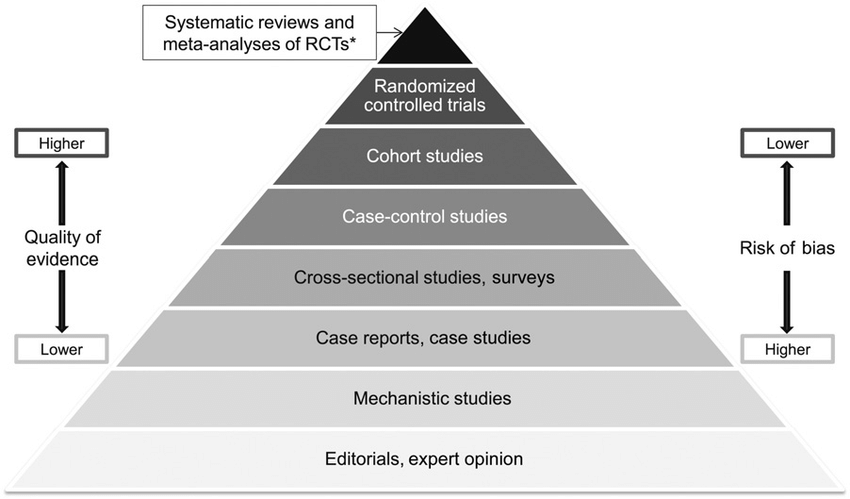
Keep in mind that one of these studies is a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and the other is a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. These are considered excellent quality evidence in the hierarchy of evidence.
Vitamin E Complex Alpha-Tocopherol Reduces Inflammation
In their 2020 meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of vitamin E supplementation, Asbaghi and colleagues found that supplementing the diet with the tocopherol portion of the vitamin E complex reduces markers of inflammation.

This meta-analysis found that supplementing with vitamin E containing alpha-tocopherol reduced the following markers of inflammation:
- C-reactive protein (CRP), a powerful predictor of cardiovascular disease death.
- Interleukin-6 (IL-6)
- Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha)
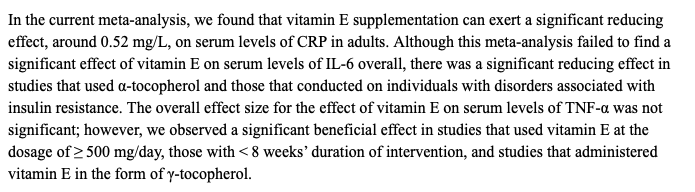
Vitamin E alpha-tocopherol supplementation at 300-600 mg/d for at least 8 weeks was found to be more effective for reduction of CRP than other lifestyle interventions and bariatric surgery. Vitamin E supplementation reduced CRP by 0.52 mg/L, compared to only 0.13 mg/L reductions for lifestyle interventions and 0.16 mg/L reductions for bariatric surgery.
Vitamin E supplementation with alpha-tocopherol (as compared to other tocopherols) was most effective at reducing IL-6.
Vitamin E supplementation at doses greater than 500 mg per day was most effective at reducing TNF-alpha. Both alpha- and gamma- tocopherol were effective at reducing TNF-alpha.
Vitamin E Complex Tocotrienols Reduce Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
In their 2021 systematic review of randomized controlled trials of tocotrienol supplementation, Khor and colleagues found evidence that supplementing vitamin E complex tocotrienols reduces inflammation and oxidative stress.

Khor and colleagues found evidence that vitamin E complex tocotrienols supplementation may reduce CRP if the supplement includes ∂-tocotrienol. This was based on a single study that used only ∂-tocotrienol, so we don't have RCT evidence regarding the effects of the other toctrienols on CRP yet.
They also found evidence that supplementing vitamin E complex tocotrienols at 400 mg/day might reduce malondialdehyde levels. Malondialdehyde (MDA) is a marker for oxidative stress that has been found in heated sunflower and palm oils. It is highly reactive and potentially mutagenic. MDA has been found in tissue sections of joints affected by osteoarthritis.
Vitamin E Complex Supplementation Recommendation
In a previous post on vitamin E I explained why I recommend the Nature's Sunshine Vitamin E Complete over other commonly available vitamin E complex supplements.
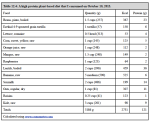
|
Nature's Sunshine Vitamin E Complete provides 268 mg of total vitamin E, including d-alpha, beta, delta and gamma tocopherols, and alpha, beta, delta and gamma tocopherols per capsule. This meta-analysis suggests that a dosage of 2-3 capsules daily would produce the maximum anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects reported in these two studies. |
 |
That dose may be optimal for individuals suffering from inflammatory disorders until the disorders are in remission. At that point a dose of 1 capsule daily would likely be more than adequate to prevent recurrence, provided one is consuming a healthy diet.
Recent Articles
-
High Protein Chocolate Tofu Pudding
Jul 01, 24 12:41 PM
A delicious high protein chocolate tofu pudding. -
Vegan Macrobiotic Diet For Psoriasis
Sep 05, 23 06:36 PM
Vegan macrobiotic diet for psoriasis. My progress healing psoriasis with a vegan macrobiotic diet. -
How Every Disease Develops
Aug 04, 23 06:22 PM
How every disease develops over time, according to macrobiotic medicine. -
Why Do People Quit Being Vegan?
Jun 28, 23 08:04 PM
Why do people quit being vegan? How peer pressure and ego conspire against vegans. -
Powered By Plants
Mar 16, 23 08:01 PM
Powered By Plants is a book in which I have presented a lot of scientific evidence that humans are designed by Nature for a whole foods plant-based diet. -
Carnism Versus Libertarianism
Dec 30, 22 01:55 PM
Carnism Versus Libertarianism is an e-book demonstrating that carnism is in principle incompatible with libertarianism, voluntaryism, and anarchism. -
The Most Dangerous Superstition Book Review
Nov 15, 22 08:46 PM
Review of the book The Most Dangerous Superstition by Larken Rose. -
Plant-Based Diet Is Best For Health Protection: Meta-Review
Oct 17, 22 11:22 AM
A plant-based diet is best for health promotion according to a meta-review of more than 300 reviews published 1950-2013.